目的
制訂可用原型個體生成的物件類型,爾後只須複製此原型即可生成新物件。
Specify the kinds of objects to create using a prototypical instance and create new objects by copying this prototype.
適用
當系統必須與成品物件的生成、組裝、表達方式保持獨立時,以及下面三種情況之一:
- 在Runtime才指明欲實體化哪一種類別時(如:動態載入);或
- 避免造出與成品物件平行的一整族factory類別階層時;或
- 當類別的物件個體只可能處於少數幾種可能的狀態時,替各種可能的狀態安置原型個體讓人複製,會比手動實體化類別來得方便。
結構及成員
Collaborations: Client叫Prototype自我複製一份。
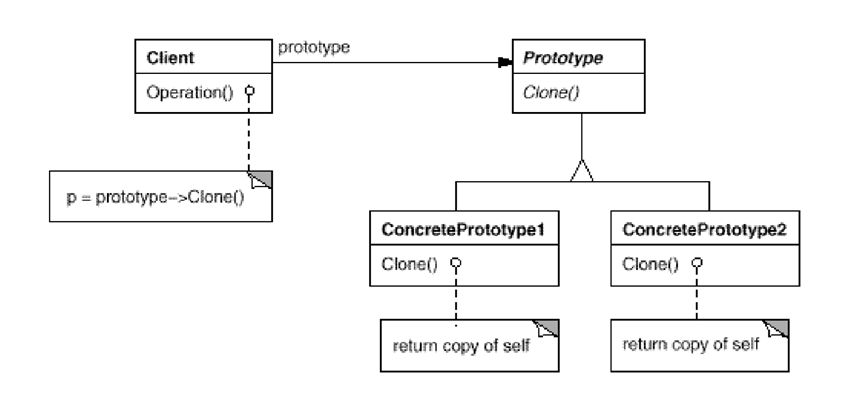
//必須實作Cloneable且必須擲出錯誤訊息
public interface Prototype extends Cloneable {
public void getName();
public Prototype clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
}
//所有try-catch皆為必須
public class ConcretePrototype implements Prototype{
public Prototype clone(){
try {
return (Prototype) super.clone();
} catch(CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}影響結果
好處
壞處
實作
使用原型個體管理者
- 若系統內原型個體的數量不固定(會動態產生及撤銷)。
- 用登錄表註冊存取原型個體後再複製。
製作clone()方法
- 複製物件時是否會遞迴地將內含的個體變數也一併拷貝?
- 若物件有save()和load()方法,就能先將物件save到記憶體緩衝區,再從緩衝區load到另一個物件身上。
初始化複製品
- clone()方法通常不允許傳遞初始化參數。
- 可另外寫Initialize()方法進行參數的設定。
- 若clone()方法是深層拷貝,則要先刪除內部的複製品。
Example: Shape
Class: Shape
package shape;
public abstract class Shape implements Cloneable {
private String id;
protected String type;
abstract void draw();
public String getType(){
return type;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Object clone() {
Object clone = null;
try {
clone = super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return clone;
}
}Class: Rectangle
package shape;
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
public Rectangle(){
type = "Rectangle";
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle::draw() method.");
}
}Interface: Square
package shape;
public class Square extends Shape {
public Square(){
type = "Square";
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Square::draw() method.");
}
}Class: Circle
package shape;
public class Circle extends Shape {
public Circle(){
type = "Circle";
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Circle::draw() method.");
}
}Class: ShapeCache
package shape;
import java.util.Hashtable;
public class ShapeCache {
private static Hashtable<String, Shape> shapeMap = new Hashtable<String, Shape>();
public static Shape getShape(String shapeId) {
Shape cachedShape = shapeMap.get(shapeId);
return (Shape) cachedShape.clone();
}
// for each shape run database query and create shape
// shapeMap.put(shapeKey, shape);
// for example, we are adding three shapes
public static void loadCache() {
Circle circle = new Circle();
circle.setId("1");
shapeMap.put(circle.getId(),circle);
Square square = new Square();
square.setId("2");
shapeMap.put(square.getId(),square);
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle();
rectangle.setId("3");
shapeMap.put(rectangle.getId(), rectangle);
}
}Class: PrototypePatternDemo
package shape;
public class PrototypePatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShapeCache.loadCache();
Shape clonedShape = (Shape) ShapeCache.getShape("1");
System.out.println("Shape : " + clonedShape.getType());
Shape clonedShape2 = (Shape) ShapeCache.getShape("2");
System.out.println("Shape : " + clonedShape2.getType());
Shape clonedShape3 = (Shape) ShapeCache.getShape("3");
System.out.println("Shape : " + clonedShape3.getType());
}
}Result:
Shape : Circle
Shape : Square
Shape : Rectangle
